|
|
|
Self - Induction |
|
When current
in a coil increases or decreases, there is a change in magnetic
flux linking the coil. Hence, an e.m.f.
is induced in the coil. This is called self - induced e.m.f.
(es) and the process is it opposes the cause
the has produced it. Now the causes
of this induced e.m.f. is the change
in magnetic flux through the coil (i.e. change of current
in the coil). Hence, the induced e.m.f.
will oppose the change of current in the coil. If current
in the coil is decreasing the induced e.m.f. will oppose the decrees in current.
|
|
|
The phenomenon of e.m.f. in a thermocouple when its two junction
are at different temperature is known as Seebeck Effect. |
|
 |
|
|
Fig
(a) |
|
|
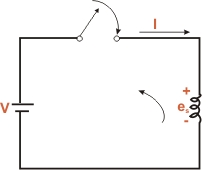
Illustration:
Figure illustrates the phenomenon of self-induction. In Fig
(a), closing the switch is an attempt to increase the current
in the coil (i.e. to change it from zero to some positive
value). As a result, e.m.f. esis induced in the
coil in such a direction to oppose the increase in current
i.e. induced e.m.f. acts in a direction opposite to that of
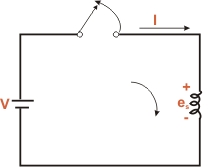
applied voltage V. In Fig (b),the opening of switch is an
attempt or reduce the current in the coil (i.e. to change
it from some positive value to zero). Again e.m.f.esis
induced in the direction of the applied voltage V.
|
|
 |
|
Fig
(b) |
|
|
It
may be noted that the e.m.f. induced
in a coil will persist so long as the current in the coil
is changing. Thus in the above two cases, the induced voltage
eventually reduces to zero because there is no continuous
attempt to change the current beyond the instant that the
switch is closed or opened.
|
|